As an adventurous spirit and an avid boater, the tranquility of the water is your hallowed escape; yet hidden amid the waves can be a silent, invisible danger – carbon monoxide. This article paints a detailed picture, illuminating opportunities for you to safeguard against this odorless intruder. It guides you, like a well-versed sailor navigating treacherous waters, on how to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning aboard your vessel, ascertaining that your time afloat remains swathed in the brilliance of joy, safety, and serenity. “Best Ways to Prevent Carbon Monoxide Poisoning on Boats” is your compass towards a safer boating adventure.

Understanding Carbon Monoxide (CO)
What is Carbon Monoxide?
Carbon Monoxide or CO, as it is commonly known, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is formed as a byproduct when fuel is burned by vehicles, small engines, stoves, lanterns, grills, fireplaces, gas ranges, or furnaces. Despite its seemingly harmless appearance, it is highly toxic for humans and animals, posing a significant health risk even in small quantities.
How is Carbon Monoxide Toxic?
Carbon Monoxide is toxic due to its ability to bind with hemoglobin in your blood, preventing oxygen from reaching your tissues and organs. If you inhale a large quantity of CO, it can replace much of the oxygen in your blood, causing oxygen deprivation or hypoxia, which can lead to serious health issues or even death.
Why is Carbon Monoxide a Hazard on Boats?
Carbon Monoxide is specifically hazardous on boats due to the presence of engines, generators, and other fuel-burning equipment onboard. Because CO is colorless and odorless, the buildup of this lethal gas often remains undetected until it’s too late. Furthermore, the boat’s motion can often trap CO in enclosed or semi-enclosed areas on the vessel, increasing the potential risk.
Identify Sources of Carbon Monoxide on Boats
Engine Exhaust Outlets
One of the main sources of CO on boats is the engine exhaust outlets. Incomplete combustion in the engine can produce large amounts of CO that is expelled through the exhaust. If these outlets are not properly ventilated or are blocked, the gas could enter the boat’s interior, posing a serious risk.
Generators
Generators utilized on boats, especially propane or gasoline-powered ones, can also produce dangerous levels of CO. They should be placed in well-ventilated areas and be checked regularly for proper functioning.
Heating Systems
Onboard heating systems, particularly those that use propane or diesel, can generate CO if they are not operating correctly. Any issues with these systems should be remedied as soon as possible to avoid CO accumulation.
On-board Kitchen Equipment
On-board kitchen equipment poses a significant risk for CO exposure on boats. Items like gas stoves, ovens, and grills must be adequately vented and used with caution to prevent hazardous levels of CO build-up.
Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Daily Inspection of the Boat
Regular, daily inspections of the boat can significantly minimize the risk of CO poisoning. You should check for visible exhaust while the engines or generators are running and look for blocked exhaust outlets that could trap fumes on board.
Regular Engine Maintenance
Frequent engine maintenance is vital to ensure they are running efficiently and safely. Annual servicing by professionals is recommended to keep the engines’ emissions within acceptable safety levels.
Proper Upkeep of Heating and Cooking Systems
Ensure that all heating and cooking systems are kept in good working order and receive regular service. Inspect them for corrosion, wear, and tears, which could affect their performance and contribute to CO production.
Checking for Blockages in Exhaust Outlets
Regular inspections should also focus on the exhaust outlets of the boat. Check for blockages or damage that could lead to CO being trapped and seeping into the boat’s interior.
Proper Ventilation
Need for Proper Ventilation on Boats
Proper ventilation is mandatory to disperse any CO build-up. Any enclosed or semi-enclosed spaces on the boat should be fitted with efficient ventilation systems to ensure constant air exchange.
Checks for Adequate Ventilation
Regular checks should be made to ensure that all ventilation systems are functioning correctly. Check for any obstructions or damages to these systems and rectify any issues promptly to maintain a safe environment.
Measures to Increase Ventilation
Consider installing extra fans or vents, particularly in areas that may trap CO, such as underneath seats or behind canvas enclosures. Remember that the boat’s design and movement can create areas where CO can accumulate.
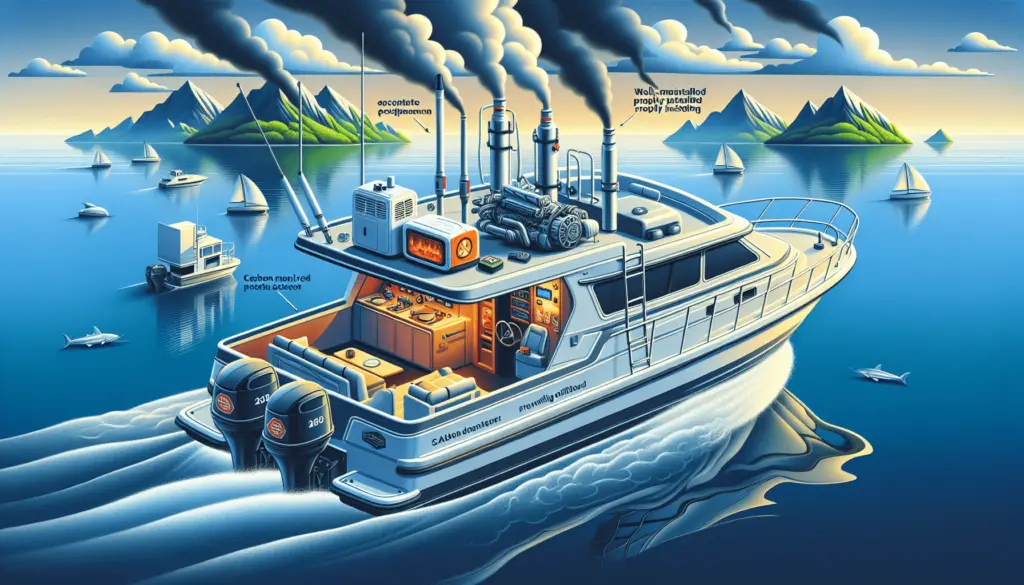

Proper Installation and Use of Equipment
Right Placement of Exhaust Outlets
The placement of exhaust outlets should be such that they are far away from enclosed or semi-enclosed spaces. The installation should also be done keeping in mind the wind direction and boat movement to prevent CO from being drawn into the boat.
Using Appliances as Intended by Manufacturers
Follow manufacturers’ instructions when using appliances. Many kinds of equipment are designed for outdoor use only and can produce lethal levels of CO if used in an unventilated space.
Awareness About Dangers of Using Certain Equipment Inside Cabins or Enclosed Spaces
Never use charcoal grills, camping stoves, or gas lanterns inside a cabin or enclosed space. These devices produce CO and lack a proper venting system for enclosed areas, leading to dangerous accumulation.
Carbon Monoxide Detectors
Importance of Installing Carbon Monoxide Detectors
Carbon Monoxide detectors are crucial for CO safety on boats. They can alert you to a CO build-up in the early stages, potentially averting a serious incident.
Proper Placement of Detectors
Detectors should be positioned in or near sleeping areas and other enclosed or semi-enclosed spaces. Follow the detector manufacturer’s instructions for additional placement recommendations.
Regular Checks and Maintenance of Detectors
Regular maintenance of CO detectors is crucial to ensure that they are continually effective. Test your detectors frequently, replace batteries as needed, and ensure they are less than 7 years old, as the sensors degrade over time.
Recognizing Symptoms of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Early Symptoms of CO Poisoning
Early symptoms of CO poisoning can include headache, dizziness, confusion, fatigue, and nausea. It’s important to be aware of these symptoms, which can often be mistaken for seasickness or intoxication.
Severe Signs of CO Poisoning
Severe signs of CO poisoning can include severe headaches, weakness, seizures, chest pain, and unconsciousness, amongst other symptoms. If someone on board exhibits these signs, immediate medical attention is required.
How to Respond if Symptoms are Observed
If you observe symptoms of CO poisoning, immediately move the person to fresh air and seek medical help. Do not underestimate the situation as CO poisoning can quickly become life-threatening.
Training and Education for Boat Operators and Passengers
Importance of Training for CO Poisoning Prevention
Training boat operators and passengers about CO poisoning prevention is critical. Comprehensive knowledge on the source, symptoms, and emergency response can save lives.
Key Points for Education Sessions
The key points for training sessions should include: awareness of CO, understanding the sources of CO on a boat, being able to recognize symptoms of CO poisoning, proper use of equipment, and knowledge of emergency procedures.
Interactive Training Methods
To ensure effective learning, consider using interactive training methods such as drills, engaging videos, games, quizzes, and demonstrations of safety equipment.
Emergency Response in Case of CO Poisoning
First Aid Steps
Immediate first aid procedures include moving the person to a fresh air location, administering oxygen if available, and initiating CPR until medical help arrives.
Emergency Contact Numbers
Keep emergency contact numbers, including that of the nearest maritime rescue center, easily accessible and ensure all passengers are aware of these.
Regular Drill Sessions
Regularly holding emergency drill sessions can prepare everyone on board to react quickly and efficiently in a crisis. These drills should simulate common emergencies, including a CO poisoning scenario.
Compliance with Safety Standards and Regulations
Understanding the Local Maritime Safety Regulations
Familiarize yourself with your local maritime safety regulations. Complying with these regulations can help ensure that all onboard are safe from potential hazards, including CO poisoning.
Regular Safety Audits
Conduct regular safety audits to identify and resolve potential issues, check the functioning of detectors, inspect for possible CO sources, and ensure that the boat is fittingly maintained.
Keeping Safety Equipment and First Aid Kits Updated
Regularly update your safety equipment and first aid kits. Ensure all passengers know how to use this equipment and make sure they are easily accessible in case of an emergency. By following this advice, you can ensure a safe and enjoyable boating experience.