“It’s time to take matters into your own hands and learn how to perform a compression test on your boat engine. In this helpful guide, you’ll find everything you need to know to carry out this essential task with confidence and ease. Understand why it’s important, what tools you will need, and meticulously detailed steps to ensure you cover all the bases. Enhancing your boat maintenance skills has never been easier or more accessible. Get ready to embark on a journey of becoming your boat’s best mechanic.”
Understanding the Basics of a Compression Test
Definition of a Compression Test
A compression test is a simple, yet crucial diagnostic method often used in mechanical engines, such as boat engines. The test works by measuring the pressure (often termed as ‘compression’) generated by the pistons in an engine’s cylinders. This compression is a result of the piston’s movement, which forces air and fuel into a small space in the cylinder. This mixture is then ignited by a spark, leading to a compression of gases and hence powering the engine.
Importance of a Compression Test
A compression test serves diverse important functions. First and foremost, it helps gauge the condition of the internal parts of the engine, such as the valves, piston rings, and cylinders, by measuring the pressure they create. Moreover, it can aid in identifying any significant problems in these parts. From a functional standpoint, good engine compression is integral for proper engine operation. Thus, a compression test is an indispensable part of engine maintenance and troubleshooting.
Understanding the Mechanics of Compression Testing
To conduct a compression test, a pressure gauge is attached to the place of the spark plug in the cylinder. Once the engine is cranked, the pressure created by the pistons’ upward stroke is measured. This process is repeated for all the cylinders in an engine, and the readings are compared. Understanding how the mechanics work is essential for conducting accurate, effective compression tests.
Identifying the Need for a Compression Test
Common Symptoms of Compression Issues
Before we discuss conducting a compression test, let’s pinpoint the common symptoms that necessitate it. These range from decreased performance (including power loss and reduced fuel efficiency) to increased exhaust smoke and overheating issues. Engine misfires and inability to start can also indicate underlying compression troubles.
Reasons for Performing a Compression Test
Aside from these symptoms, a compression test is a regular part of preventive maintenance. It can help identify potential problems before they progress into more severe, costly repairs. Additionally, a compression test can assure you of the good health of your engine, particularly beneficial when purchasing a used boat engine.
How Often to Perform a Compression Test
The frequency of a compression test can vary depending on the engine’s use, age, and general condition. However, as a rule of thumb, conducting one annually or for every 100 hours of engine operation can help maintain peak engine performance.
Equipment Needed for a Compression Test
Essential Tools for a Compression Test
The tools needed for a compression test include a compression tester, which usually comes with a built-in pressure gauge, various adapters to fit different spark plug sizes, and a remote start switch or a helper to crank the engine.
Where to Acquire Compression Test Tools
Compression test tools can be found in most automobile stores, as well as online. It is important to research the specific tools required for your particular boat engine model before purchasing to ensure compatibility.
How to Properly Handle and Care for Your Compression Test Tools
Once you acquire the tools, proper handling is important to ensure their longevity. Always clean them before and after use, store in a cool dry place, and avoid forceful handling that could lead to damages.
Pre-Test Preparation
Checking for Engine Readiness
Before conducting the test, ensure the boat engine is in good working condition. This means checking the oil and coolant levels, ensuring the battery is fully charged, and that there are no leaks or other visible damage.
Safety Measures to Observe Before Beginning a Compression Test
Conducting a compression test involves handling potentially hot or live components. Always let the engine cool down before beginning and wear safety gear, such as thick gloves and eye protection. Prevent accidental starts by removing the ignition coil connector.
How to Prepare Your Boat Engine for a Compression Test
Start by warming up the engine, as a cold engine can skew the results. Next, all spark plugs need to be removed to perform the test on each cylinder individually.
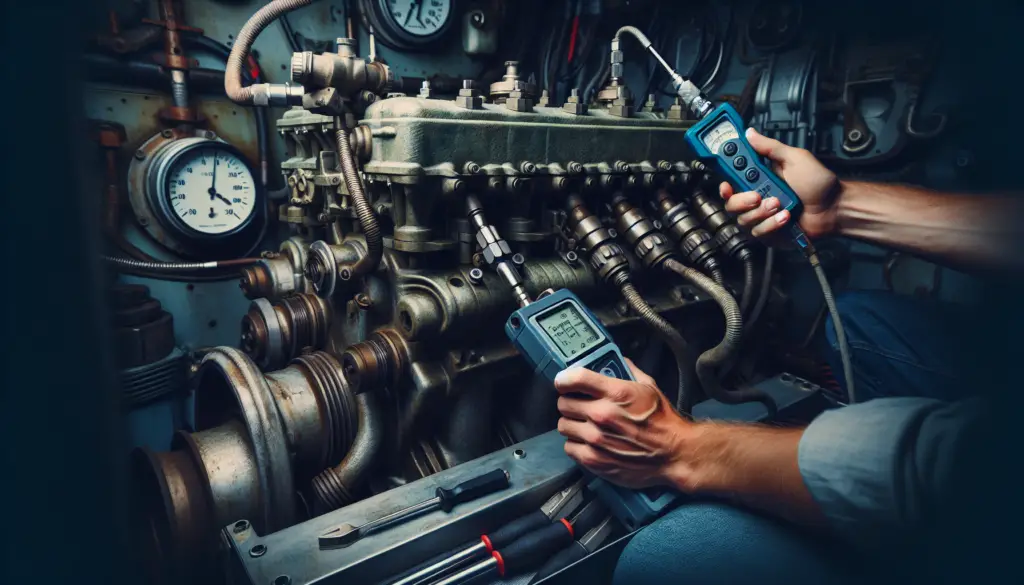

Executing the Compression Test
Step-by-step Guide to Performing a Compression Test
After warming up and preparing the engine, attach the compression tester to the first cylinder. Use the remote start switch or have your assistant crank the engine for about five seconds. Note the pressure on the gauge and repeat this process for each cylinder.
Common Errors to Avoid While Performing a Compression Test
Common errors include testing a cold engine, partial throttle opening, and incorrect gauge reading. Make sure your methodology is accurate to yield reliable results.
How Long a Compression Test Typically Takes
On average, a compression test can take about an hour. This time can vary depending on the number of cylinders in your engine and your familiarity with the process.
Interpreting Compression Test Results
Understanding Compression Test Readings
The readings should typically fall within 10% of each other. Anything above this could indicate a problem within the specific cylinder.
What is a Good Compression Reading
A good reading should typically be above 100 PSI. However, this can vary based on your engine type. It is always best to refer to your engine manufacturer’s guidelines for exact figures.
How to Tell if There’s a Problem with Your Compression Test Results
If your readings are low or inconsistent across cylinders, this indicates problems. These could be a result of worn-out piston rings, a faulty cylinder, or damage to the cylinder head, among others.
Troubleshooting Based on a Compression Test
Common Issues Indicated by Compression Tests
Compression test results can reveal multiple issues such as a blown head gasket, a cracked cylinder wall, damaged piston rings or valves.
How to Tackle Compression-Related Issues
Most compression-related issues are complex and require professional repairs. However, some like replacing spark plugs or a head gasket may be doable if you’re comfortable with engine repairs.
When to Seek Professional Help for Compression Troubles
Highly technical issues should be handled by a professional to avoid causing further damage to the engine. If your test reveals negative results and you’re unsure of the next steps, consult a professional.
Preventive Measures for Healthy Compression
Routine Practices for Maintaining Good Compression
This includes regular oil changes, using good quality fuel, regularly checking and replacing worn-out spark plugs, filters, and ensuring Regular maintenance.
Factors that Affect Engine Compression
Compression can be affected by time, wear, usage, and neglect. Regularly running the engine and looking out for early symptoms can aid in maintaining good compression.
How Regular Maintenance Plays a Role in Compression Health
Regular maintenance ensures the engine parts are in top form, which positively affects the compression. Ignoring maintenance will inevitably lead to compression issues.
Training and Skill Acquisition for Compression Testing
Where to Learn Compression Testing
Basic compression testing can be self-taught through manuals, online resources, and trials. For more complex learning, consider vocational mechanical training courses or apprenticeships.
Training Requirements for Effective Compression Testing
Theoretical understanding along with hands-on exposure is key to mastering compression testing. Learning engine mechanics, gaining an understanding of different boat engines, and actual testing practice are generally required.
Benefits of Understanding and Performing Your Own Compression Test
Being able to conduct your own compression test can save you maintenance costs, help to identify issues early, and expand your technical skills.
Legal and Environmental Considerations
Legal Concerns Regarding Compression Testing on Your Own
While there are typically no legal concerns, always refer to your local laws and follow manufacturer’s guidelines while performing maintenance to avoid infringing on warranties.
How to Dispose of Materials After a Compression Test
Used spark plugs or other engine parts should be disposed of responsibly according to local regulations.
Environmental Impact of Regular Compression Tests
Regular compression checks can actually benefit the environment by aiding in maintaining optimal engine performance, which in turn, helps in reducing harmful emissions.
In conclusion, understanding and being able to perform a compression test is an invaluable skill for any boat engine owner. With the right equipment and a little practice, you can keep your engine in top-notch condition.